etcd-file-system.md 3.5 KB
#Etcd File System
Structure
Node
In etcd, the node is the base from which the filesystem is constructed. etcd's file system is Unix-like with two kinds of nodes: file and directories.
- A file node has data associated with it.
- A directory node has child nodes associated with it.
All nodes, regardless of type, have the following attributes and operations:
Attributes:
- Expiration Time [optional]
The node will be deleted when it expires.
- ACL
The path to the node's access control list.
Operation:
- Get (path, recursive, sorted)
Get the content of the node
- If the node is a file, the data of the file will be returned.
- If the node is a directory, the child nodes of the directory will be returned.
- If recursive is true, it will recursively get the nodes of the directory.
- If sorted is true, the result will be sorted based on the path.
- Create (path, value[optional], ttl [optional])
Create a file. Create operation will help to create intermediate directories with no expiration time.
- If the file already exists, create will fail.
- If the value is given, set will create a file.
- If the value is not given, set will crate a directory.
- If ttl is given, the node will be deleted when it expires.
- Update (path, value[optional], ttl [optional])
Update the content of the node.
- If the value is given, the value of the key will be updated.
- If ttl is given, the expiration time of the node will be updated.
- Delete (path, recursive)
Delete the node of given path.
- If the node is a directory:
- If recursive is true, the operation will delete all nodes under the directory.
- If recursive is false, error will be returned.
- TestAndSet (path, prevValue [prevIndex], value, ttl)
Atomic test and set value to a file. If test succeeds, this operation will change the previous value of the file to the given value.
- If the prevValue is given, it will test against previous value of
the node.
- If the prevValue is empty, it will test if the node is not existing.
- If the prevValue is not empty, it will test if the prevValue is equal to the current value of the file.
- If the prevIndex is given, it will test if the create/last modified index of the node is equal to prevIndex.
- Renew (path, ttl)
Set the node's expiration time to (current time + ttl)
ACL
Theory
Etcd exports a Unix-like file system interface consisting of files and directories, collectively called nodes. Each node has various meta-data, including three names of the access control lists used to control reading, writing and changing (change ACL names for the node).
We are storing the ACL names for nodes under a special ACL directory. Each node has ACL name corresponding to one file within ACL dir. Unless overridden, a node naturally inherits the ACL names of its parent directory on creation.
For each ACL name, it has three children: R (Reading), W (Writing), C (Changing)
Each permission is also a node. Under the node it contains the users who have this permission for the file referring to this ACL name.
Example
[TODO]
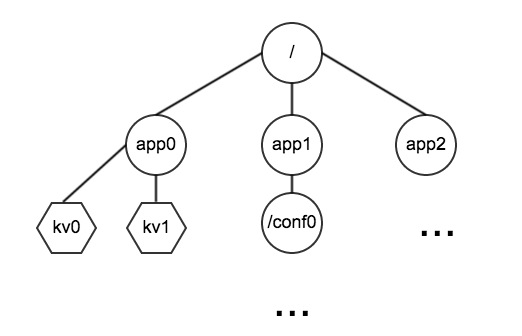
Diagram
[TODO]
Interface
Testing permissions:
- (node *Node) get_perm()
- (node *Node) has_perm(perm string, user string)
Setting/Changing permissions:
- (node *Node) set_perm(perm string)
- (node *Node) change_ACLname(aclname string)
User Group
[TODO]